Tại Google Cloud, Google cam kết cung cấp cho khách hàng sự lựa chọn hàng…
How to protect your Gmail account and personal information from being hacked
Gmail is an email service that is increasingly used in offices and schools with more than a billion monthly active users. Not only is it used to send and receive mail, Gmail also plays a very big role: As a store of personal data and a "bridge" to many other applications (for example, when you use Gmail to create accounts). accounts on Facebook, LinkedIn). That's why, the protect Gmail account It's not just about protecting an email address, it's also about Protect yourself online. This article will guide you through the necessary steps to help you not fall into the situation of "losing cows to build a barn".
1/ Check the general security status of your Gmail account
1.1. Add or update account recovery options
These options may include a phone number or another email address. Although the operation is very simple, just providing this information to Google will save you a lot of trouble later. However, due to not paying attention or thinking it is not necessary, many users often lose their accounts before they know the importance of recovery information. Specifically, these communications will be used to:
- Prevent others from using your account without permission
- Send alerts if your Gmail account has suspicious activity. For example, logging in from an unknown device or address, or just granting permission to a third party to access information.
- Recover your account in case you get hacked, or naturally can't log in as usual.
Please refer to how to add or change account recovery information here.
1.2. Enable two-step verification (2-Step Verification)
As the name suggests, two-step verification will require you to double-prove that: You are the one with access to your account. Specifically, after entering your email address and password, you will have to perform one more authentication operation. It could be one of the following:
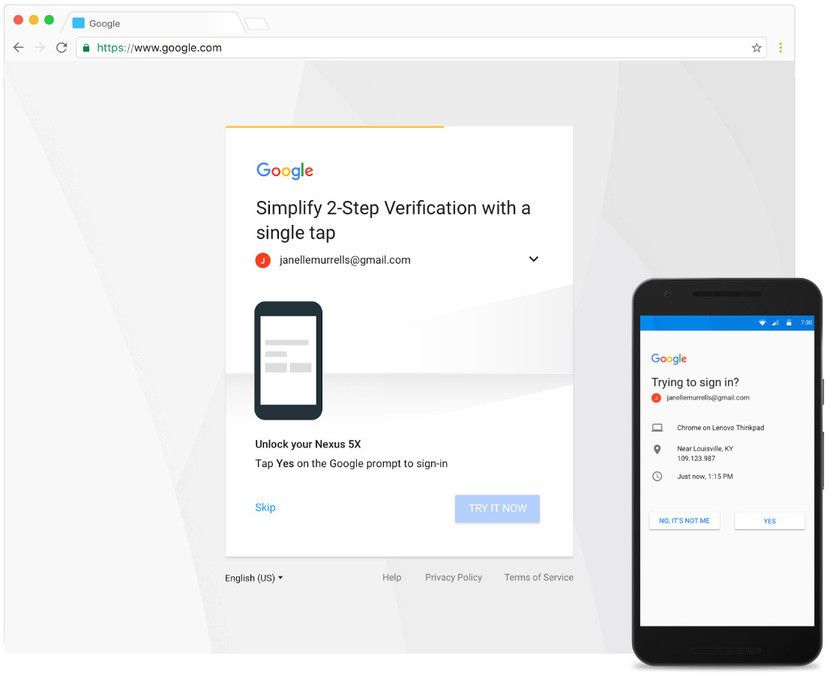
- Use Google Prompt on your phone: After completing the first authentication step, the system will send a notification to your phone to verify again with the message “Trying to sign in?” along with the details of the login (device, time, location). If so, just tap the “Yes” option on your phone. This way is not only faster, but also considered safer enter the code sent to your phone*.
*Previously you can use another way is to enter the code sent via text message. However, this way was soon caught by hackers and they also found a way to cheat to steal information. Therefore, it is best to use only one of the two methods outlined here.
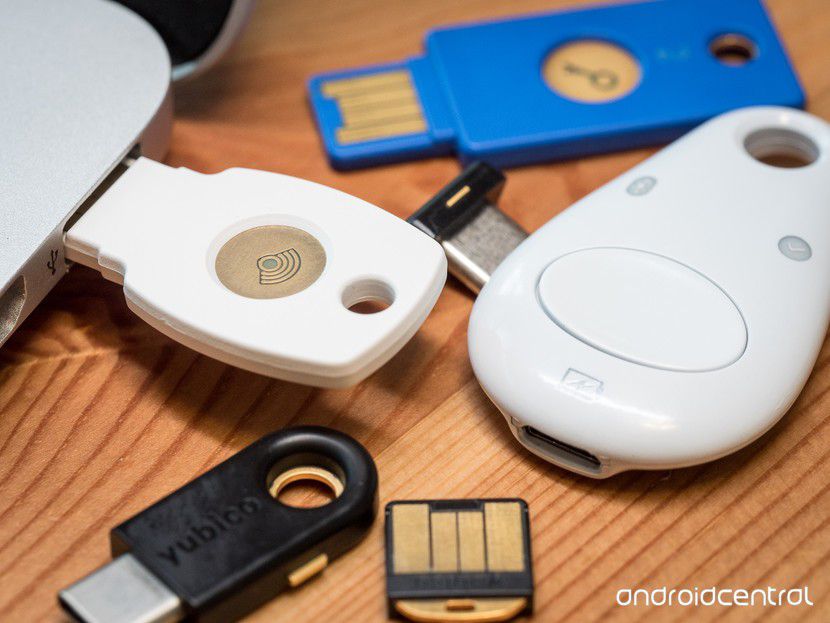
- Using a security key – Security Key: After all efforts to "digitize" everything, perhaps returning to the traditional, physical "key" method is still… the safest. This key is designed like a USB that you can easily carry and easily plug into your computer every time you need to authenticate.

1.3. Filter and remove apps that pose a risk to your data.
An email account is often used to connect to many other applications – not only social networking sites, but also used to subscribe to other services, software, and add-ons. During this registration process, the user may not pay attention to the service provider's request to access information.
For example, quite a few parties are now asking you to allow them to read emails; edit, upload some content to Google account. There will even be applications that require almost full access and they can view and change most information related to the account.
So it's important that you know and manage who has access to your account. If those are not necessary, important applications, they should be deleted.
You can click on the My Account by Google to see a list of which sites and apps have access to which parts of their data. For example the image below:
1.4. Turn on screen lock
Whether it's a computer screen or a phone screen, you should be careful and set a password. Screen lock helps protect your device from unauthorized access. Especially, if you use 2-step authentication, and the second authentication step is done on the phone, the screen lock becomes even more important.
2/ Please update the software you are using
Since the release of the software, the production unit will regularly update and fix bugs (if any) to ensure the best user experience. These updates include protecting users from potential vulnerabilities that pose a threat to cyberattacks.
Therefore, if the software you are using such as browsers, applications, operating systems, etc. has not been updated to the latest version, the risk of being attacked by hackers is completely possible.
3/ Use “strong” and “special” passwords
A very common habit of users is to use the same password for many accounts, for many different sites. Some users use many passwords, then write them all down in the Note section of the phone. This habit will have unpredictable consequences if a certain page is hacked or when the phone falls into the wrong hands.
Therefore, you need to create a strong and special password for each of your accounts.
- You might consider using a password manager app (Password manager) to generate unique passwords. (One tip to make using Gmail more convenient and secure is to use the Chrome browser developed by Google itself.)
- Protect your password from hackers: Use it Password Alert for Chrome to be sent a timely notification each time you enter your Google account password on a non-Google Web site (such as pages that masquerade as Google's).
4/ Protect yourself from suspicious messages and content
Hackers can use emails, phone messages, calls or websites and pretend to be relatives, friends, colleagues, or reputable organizations. So be wary of:
- Suspicious requests:
- Don't tell anyone to give your password to anyone. Remember that Google will never ask for your password via email, text, or phone (so do other service providers, e.g. no bank calls asking for your password or code/eToken). your).
- Do not respond to texts, emails, websites, etc. that ask you for personal or financial information.
- Do not click on links in emails, messages, or pop-ups from untrustworthy websites or senders.
- Potentially dangerous emails for information fraud (email phishing)
- Dangerous Websites: Part of the reason you should trust and use Google apps, including Chrome and Search, is because they're designed and developed to warn you about dangerous content and unwanted software (which is deliberately tricking users into installing them). You can learn more about warnings in Chrome and Search.
The operations outlined above are all important instructions that you should complete because they can support each other and protect your account in the best way. In addition, no matter what software you install or do, the most important thing is still carefulness and vigilance from the user. Wish you safe online activities
Update: Gimasys



