Tại Google Cloud, Google cam kết cung cấp cho khách hàng sự lựa chọn hàng…
Google Cloud networking: Cloud CDN
For more than a decade, Google has invested heavily in infrastructure and software to build a network that can provide great experiences to users around the world. With GCP Google Cloud, we also utilize these core technologies and infrastructure as the basis for product formation Cloud CDN, allowing businesses to deliver content to their users with class-leading bandwidth and performance. Cloud CDN will store content in locations around the world to broadcast video, store images, download game updates and many other digital applications.
In this article, let's discuss the architecture and key features of Cloud CDN to help you speed up content delivery to global users. The article will conclude with practical cases and useful references.
Cloud CDN infrastructure
Google realized early on that it was necessary to build its own systems and infrastructure to be able to keep up with the growth of network bandwidth and increase customer satisfaction. That's when we officially invested in core infrastructure and technological innovation that we continue to this day.

As a result of these investments, Google Cloud is now one of the fastest and best connected networks on the planet, reaching most Internet customers through a direct connection between Google and the provider. their network.
As part of Google Cloud, Cloud CDN will store your content locally 96 locations in the world and give 134 edge network locations, so your content is close to the user, typically within 1 network hop from the network provider.
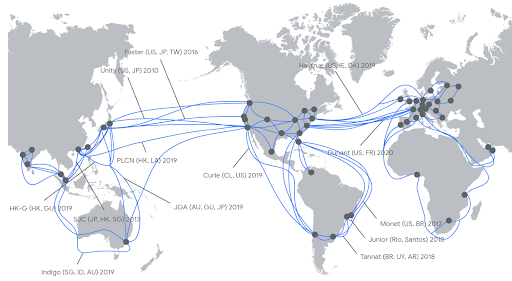
A map of Google's global network shows that Google's cables are connecting multiple continents and sub-regions. When using Cloud CDN, network traffic will go from the origin point through this network system to the network area closest to the user.
The number of points of presence (PoPs) and storage locations is very important, other factors also contribute to Cloud CDN's high performance, wide bandwidth and low latency:
- Direct network connections to most user-facing networks allow Cloud CDN to select the most optimal storage location for the origination zone.
- The Google optical network system carries network traffic that cannot be interrupted by additional points.
- Innovations like QUIC, HTTP/2, and collision control protocols like BBR, deliver high performance at the edge.
To learn more about Cloud CDN performance, take a look at these evaluation report from Citrix ITM.
Cloud CDN architecture: caching, load balancing and Google premium network
HTTP(S) Load Balancer is a distributed system that provides load balancing at the edge of Google's global network infrastructure. Cloud CDN is integrated with HTTP(S) Load Balancer at these network edges.
When your users request data, they connect to the Cloud CDN at the edge closest to them. In case of a cache match, Cloud CDN will serve it directly from one of the aforementioned 96 cache edge points around the world. In the event of a cache mismatch, Cloud CDN requests the data from its origin on GCP (which could be a storage bucket or a VM) through Google's high-performance network, and then transmits the data back to the client. rows with the same path. This way runs on Premium Network Service Tier, keeps user traffic on GCP fiber for the longest distance possible to reduce latency and increase bandwidth.
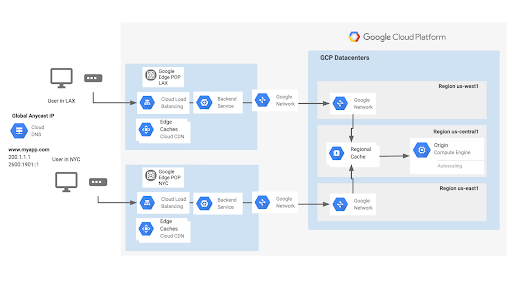
Cloud CDN features
In addition to running on Google premium fiber, Cloud CDN also offers a variety of other useful features.
First, it is extremely easy to enable Cloud CDN for a Google Cloud back-end service (a storage bucket or a VM). There are no complicated DNS rules or distributions to configure—just select a checkbox (or make an API call) to hire Google's entire distributed network infrastructure to cache and serve your content.

In addition, Cloud CDN offers many outstanding features that make it a great choice for global content delivery:
- Google premium network
- Global Anycast IP
- No-cost SSL termination
- Encryption in-transit
- Signed URLs
- Global Scale
- Logging and monitoring via Stackdriver
- Configurable cache keys
- Large object support and automatic content size optimization
- IPV6 support
Starting with Cloud CDN Since Cloud CDN is an extension of HTTP(S) Load Balancer, implementing a CDN distribution is achieved by creating a load balancer and attaching CDN caching functionality to one or more load-balanced back ends.
Cloud CDN will cache all content with appropriate caching headers, served via Anycast IP (or any domain name that has been mapped to this IP via DNS records).
Furthermore, the Cloud CDN docs list a few best practices can help you optimize your content. A few things of interest are:
- Thoughtful use of invalidations
- Adjust the expiration date of time-sensitive content
- Use custom cache keywords to improve cache match rate
- Use Versioned URL to update content
For support in configuring Cloud CDN service, please contact Gimasys:
- Hotline: Hanoi: 0987 682 505 - Ho Chi Minh: 0974 417 099
- Email: gcp@gimasys.com
- Sign up for a free trial: Here.
Source: Gimasys



