Google Cloud liên tục đổi mới và đầu tư đáng kể vào khả năng ngăn…
Integrating, embracing change with cloud data warehouse
The move from a traditional on-premises data warehouse platform to a cloud data warehouse like Google Cloud BigQuery, not merely adopting new technology. It also provides an opportunity to review existing practices and adopt new ways of working. We've noted some typical changes that teams go through to support data warehouse migration to the cloud.
For a change management framework and best practices for migrating to the cloud, you can find more details in the documentation Quản lý thay đổi trong đám mây.
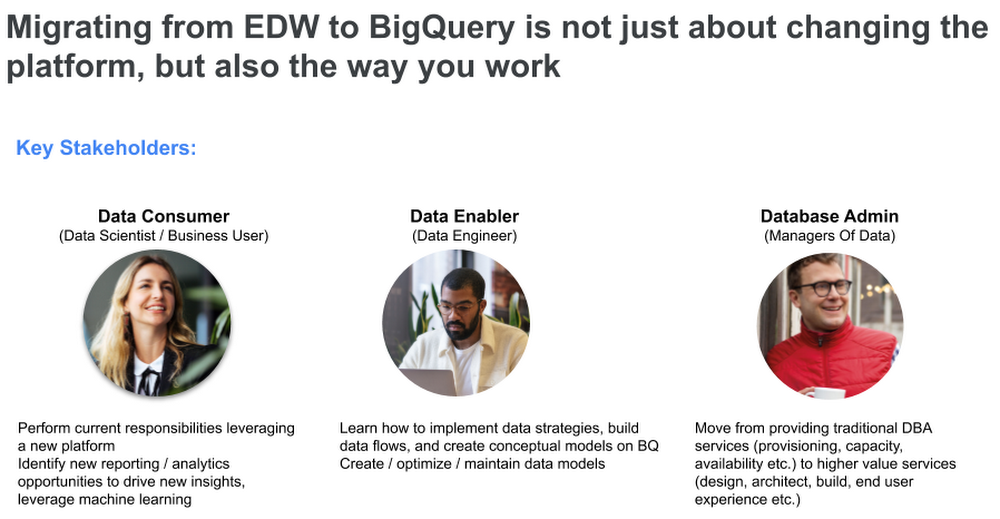
People are at the core of any change management initiative. For a data warehouse migration initiative, Google will focus on three key stakeholders involved in day-to-day use and management (although other ancillary roles may be involved):
- data consumers (Data consumers) – usually a data analyst, data scientist or business user
- Data Activator (Data enabler) – usually a data engineer or tool developer ETL
- data administrator (Data administrator) – typically a database/datastore administrator
Let's look at each stakeholder and see how their responsibilities change as their organization moves from on-premises to the cloud.
data consumers (Data consumers)
Data analysts and data scientists have many benefits from migrating to the cloud data warehouse. New datasets available, new algorithms to play with, and lower latency access options in the cloud. Typically, during a migration, existing reporting applications and BI tools are left in place to ensure minimal business disruption causing data consumers to accept relative changes. easy. However, data consumers may want to ensure that their existing reports and use cases are tested on the new platform. Therefore, it is advisable to ask them to participate in any data validation efforts. You can create a data validation group, for example.
Once migrated, data consumers can find new ways of working as they gain access to new datasets, like converting bulk reports into real-time dashboards and finding ways to turn machine learning reality for the organization. New platform capabilities eventually become the most important catalyst for change in this role. The more ambitious a data consumer is, the greater the shift will be to other roles within the organization.
Data Activator (Data enabler)
The technical capabilities of a data enabler are critical to how the cloud is successfully adopted in an organization. These individuals own the data pipelines and are deeply involved in any refactoring efforts needed to move workloads to the cloud. The roadmap may be phased depending on the technology stack that Google adopts; Proper resource planning will be important for those enabling this data. Migrating to the cloud can be a lengthy undertaking, so it's worth considering taking the time to plan, re-tool, and automate the migration.
As data enablers are restructuring and redesigning data pipelines and working alongside data consumers, they have plenty of opportunities to rethink how business processes should change. change to take advantage of real-time data ingestion, new data modeling techniques, or the permanent storage that new cloud technology offers. Data enablers can also review legacy requests that can't be accommodated due to size, data format complexity, or ETL complexity. Cloud technologies may be better suited to overcome such challenges through capabilities such as storage and resource elasticity, support for multiple data formats and storage options, and multiple storage options. tools and libraries for data processing. Additionally, adopting DevOps, container apps, or serverless compute are ways data enablers (along with data administrators) can explore to improve change rates. Changes are applied and new insights are provided to users.
data administrator (Data administrator)
Database administrators continue to play an important role even when enterprise data warehouses are hosted in the cloud. As platform owners, administrators must familiarize themselves with the cloud technology capabilities early on and drive business transformation with key stakeholders. As database administrators move data workloads to the cloud, there are next important areas to focus; an overview of governance during and after the migration, data integrity, and SLAs such as RPO and RTO. If the organization adopts a vendor-managed cloud data warehouse, the database administrator will have fewer tasks to procure and tune the underlying database. But cost versus performance optimization remains an important area for administrators to fully engage with. (See the ESG report on how to migrate to BigQuery can lower your three-year TCO by up to 52%.)
Database administrators are also freed up to deepen their understanding of the storage, networking, and compute options the cloud offers, and find ways to optimize enterprise workloads in the cloud. Admins can adopt new ways to work with machine learning notebook environments, new query engines, containerization engines, hybrid clouds, and more – there's so much to learn and optimize. optimization!
Organizations that adopt these new skills and processes have a better chance of succeeding in delivering business results in the cloud. For more information on how to streamline your business migration path, see documentation and data warehouse migration framework. You can also apply data warehouse migration incentives for help with the full migration process.
Source: Gimasys