Tại Google Cloud, Google cam kết cung cấp cho khách hàng sự lựa chọn hàng…
What is Secondary Storage? Benefits of using Secondary Storage
Một trong những thách thức cấp bách nhất của doanh nghiệp hiện nay là quyết định nên sử dụng loại lưu trữ nào và cho trường hợp sử dụng nào. Do đó, hiểu biết cơ bản về Primary Storage và Secondary Storage – trong trường hợp này là hai loại lưu trữ dữ liệu liên quan đến chiến lược sao lưu doanh nghiệp – là cần thiết. Và ở blog này, chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu sâu hơn về các khái niệm cơ bản của Secondary Storage, the ingredients and the basic benefits of using them.

What is Secondary Storage?
Secondary Storage also known as secondary storage/secondary storage, refers to the storage of data that is not as frequently accessed as the data in Primary Storage. It is a non-volatile memory medium that preserves data until it is deleted or overwritten. Secondary storage can be stored on-premises, on an external device, or in the cloud. With a wide variety of media available, secondary storage allows organizations to store data that ranges from a few megabytes to petabytes.
Cloud Storage is a business data storage service provided by Google Cloud
Types of Secondary Storage
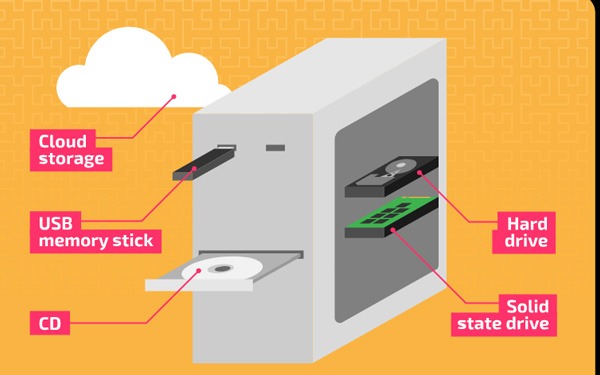
Secondary Storage needs to store data until the user actively deletes or overwrites it. This way, even if there is a power outage and all data on Primary Storage is lost, users can still restore the last backup version of the file in question. Below are the different types of Secondary Storage devices:
Hard Drive – Hard Drive
It is a secondary storage device that has the function of permanently storing and retrieving data because these hard drives are very stable. Additionally, the main function of a hard drive is to store data including operating system data, applications, documents, personal files, etc. Additionally, data storage in a hard drive is measured in gigabytes or terabytes. .
Solid State Drive – SSD
It is a secondary storage device so SSD is also a fixed memory. It is mainly used in storing and accessing data because it has faster access and high reliability. More, noiseless operation and very low power consumption.
SSDs typically use a SATA connection, which has a maximum transfer speed of 750 MB per second. The new generation SSD now connects to the motherboard's PCIe port and offers transfer speeds of up to 1.5 GB per second.
Universal Serial Bus – USB
It is a portable secondary storage device and is usually about the size of a human thumb. Universal Serial Bus connects via the computer's USB port. This is the easiest way to transfer data from one computer to another as well as a great device for storing huge amounts of data. USB provides storage capacity from 2 GB to 1 TB.
Optical mass storage
CDs and DVDs are among the most popular optical storage media. These disks can access or retrieve data for later use. It can even store software, save backup files, and store music and videos. A standard CD is capable of storing 650 MB of data or 72 minutes of music. Typically, an 80-minute CD contains 700 MB of data. However, a standard DVD is capable of storing more data than a regular CD. DVDs come in various storage capacities, starting from 4.7 GB to up to 17.08 GB. It should be noted that there is no significant difference between CD and DVD, except for storage capacity.

Benefits when used Secondary Storage
The main function of Secondary Storage is to replace/supplement Primary Storage. Data that does not need Primary Storage will be moved to Secondary Storage devices, thereby freeing up space and improving the performance of Primary Storage devices.
In particular, organizations use Secondary Storage for backup and disaster recovery as well as archival data. Regarding backups, most organizations focus on backing up mission-critical workloads – data that is accessed frequently and prioritized as part of disaster recovery plans. However, not all data is accessed or used on a regular basis. For these situations, a Secondary Storage device is the ideal choice as it provides data protection and storage features at a lower cost.
In general, Secondary Storage technology is much cheaper than Primary Storage. This type of storage can work perfectly on economical devices, which are more suitable for long-term storage.
Additionally, Secondary Storage is associated with external storage devices that are not directly connected to the server. By default, data is saved to production storage attached to the active workload or application. Keeping all data in one place can be risky. There is always the possibility of hardware and software being affected by bugs, misconfigurations, malware or other threats. Such events are detrimental to production data and negatively impact the organization. Without a proper disaster recovery and contingency strategy, such disasters can be a devastating blow to an organization's operational continuity.
Storing copies of data on a Secondary Storage platform separate from production and network environments is instrumental in preventing data loss and ensuring recovery. Another significant benefit of choosing a Secondary Storage device is cost reduction. It provides a low-cost storage layer, although the data stored may not be immediately accessible. Many organizations use Secondary Storage as part of their backup strategy to ensure a copy of valuable business data is always inaccessible over the internet or intranet.
Above are the details Secondary Storage and the benefits of using them.
Gimasys - Google's Premier Partner in Vietnam is a provider and consultant on the structure and design of the optimal Cloud solution for you. For technical support, you can contact Gimasys – Premier Partner of Google in Vietnam at the following information:
- Hotline: 0974 417 099 (HCM) | 0987 682 505 (HN)
- Email: gcp@gimasys.com
Source: Gimasys



